$q.cordova
While you are developing a Mobile App with Cordova Mode, you can access $q.cordova in your Vue files. This is an alias to the global cordova Object.
Android Tips
Android remote debugging
If you are debugging Android Apps, you can use Google Chrome Remote Debugging through a USB cable attached to your Android phone/tablet. It can be used for emulator too.
This way you have Chrome Dev Tools directly for your App running on the emulator/phone/table. Inspect elements, check console output, and so on and so forth.
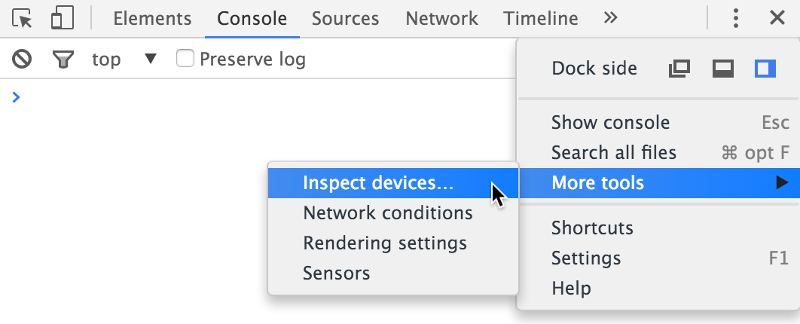
Accept Licenses
If you are having problems getting Android builds to finish and you see a message like:
> Failed to install the following Android SDK packages as some licenses have not been accepted.If this is the case you need to accept ALL the licenses. Thankfully there is a tool for this:
- Linux:
sdkmanager --licenses - macOS:
~/Library/Android/sdk/tools/bin/sdkmanager --licenses - Windows:
%ANDROID_SDK_ROOT%/tools/bin/sdkmanager --licenses
Android SDK not found after installation of the SDK
WARNING
The environmental variable ANDROID_HOME has been deprecated and replaced with ANDROID_SDK_ROOT. Depending on your version of Android Studio you may need one or the other. It doesn’t hurt to have both set.
Some newer Debian-based OS (e.g. ubuntu, elementary OS) might leave you with a Android SDK not found. after you installed and (correctly) configured the environment. The output might look similar to this:
$ cordova requirements
Requirements check results for android:
Java JDK: installed 1.8.0
Android SDK: installed true
Android target: not installed
Android SDK not found. Make sure that it is installed. If it is not at the default location, set the ANDROID_HOME (or ANDROID_SDK_ROOT) environment variable.
Gradle: not installed
Could not find gradle wrapper within Android SDK. Might need to update your Android SDK.
Looked here: /home/your_user/Android/Sdk/tools/templates/gradle/wrapper
Error: Some of requirements check failedThis could have two different reasons: Usually the paths aren’t configured correctly. The first step is to verify if your paths are set correctly. This can be done by running the following commands:
$ echo $ANDROID_HOME
# or
$ echo $ANDROID_SDK_ROOTThe expected output should be a path similar to this $HOME/Android/Sdk. After this run:
$ ls -la $ANDROID_HOME
# or
$ ls -la $ANDROID_SDK_ROOTTo ensure the folder contains the SDK. The expected output should contain folders like ‘tools’, ‘sources’, ‘platform-tools’, etc.
$ echo $PATHThe output should contain each one entry for the Android SDK ‘tools’-folder and ‘platform-tools’-tools. This could look like this:
/home/your_user/bin:/home/your_user/.local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/home/your_user/Android/Sdk/tools:/home/your_user/Android/Sdk/platform-toolsIf you ensured your paths are set correctly and still get the error on
cordova requirementsyou can try the following fix: Replacing the Android Studio ‘tools’ folder manually
Android Studio
In Android Studio (if you open it on /src-cordova/platforms/android), you will be greeted with a message recommending to upgrade the Gradle version. DO NOT UPGRADE GRADLE as it will break the Cordova project. Same goes for any other requested upgrades.

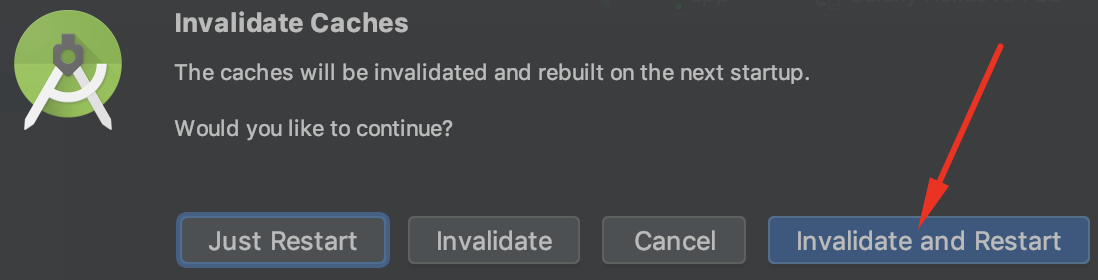
If you encounter any IDE errors then click on File > Invalidate caches and restart.
Setting up device on Linux
You may bump into ?????? no permissions problem when trying to run your App directly on an Android phone/tablet.
Here’s how you fix this:
# create the .rules file and insert the content
# from below this example
sudo vim /etc/udev/rules.d/51-android.rules
sudo chmod 644 /etc/udev/rules.d/51-android.rules
sudo chown root. /etc/udev/rules.d/51-android.rules
sudo service udev restart
sudo killall adbThe content for 51-android.rules:
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0bb4", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0e79", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0502", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0b05", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="413c", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0489", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="091e", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="18d1", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0bb4", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="12d1", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="24e3", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="2116", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0482", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="17ef", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="1004", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="22b8", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0409", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="2080", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0955", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="2257", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="10a9", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="1d4d", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0471", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="04da", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="05c6", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="1f53", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="04e8", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="04dd", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0fce", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0930", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="19d2", MODE="0666"
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="1bbb", MODE="0666"Now running adb devices should discover your device.
Post-build debugging
There are intermediate states to help with debugging, between quasar dev and distributing a completed app. If your app works fine on quasar dev but is not running properly after quasar build, you have two options:
- go to your
src-cordovadirectory andcordova run [platform].- You will be running the final build, but you can still use Chrome DevTools Remote Debugging with a wired connection (see above), to inspect the internal web internals. You cannot do this while running the .apk file.
- For more detail, read the Cordova platform guide and the CLI reference
- open Android Studio and watch the Logcat
- Here you can watch everything related to the app and its interaction with the underlying Android OS. After opening your Cordova project in Android Studio, go to
Run…Debugfrom the top menu. Android Studio will ask you to confirm the device or emulator, then will deploy the app. In the bottom window, chooseLogcatYou may want to use the filters to reduce the volume of messages. You should see[your app id].MainActivity.onCreate()signifying the app launch, then various messages related to your app functionality. - Note: this should be for experienced Android developers only. If your app is not functioning properly, it is much more likely that
quasar devorcordova runcan reveal the issue.
- Here you can watch everything related to the app and its interaction with the underlying Android OS. After opening your Cordova project in Android Studio, go to
Important!
If you find a bug using one of the above methods, do not edit the output files (probably the www folder) directly, as they will soon be overwritten. Go back to your quasar source, fix the bug, then re-run quasar build.
iOS Tips
Device type not found
If you get this error while running $ quasar dev -m cordova -T ios:
No target specified for emulator. Deploying to undefined simulator
Device type "com.apple.CoreSimulator.SimDeviceType.undefined" could not be found.Then it means you need to specify an emulator. Depending on your Cordova CLI version, here are some examples:
$ quasar dev -m cordova -T ios -e iPhone-X,12.2
# or with older versions of Cordova CLI installed on your machine:
$ quasar dev -m cordova -T ios -e iPhone-X,com.apple.CoreSimulator.SimRuntime.iOS-12-2Enabling modern build
By default, Xcode modern build for iOS is disabled due to Cordova issues. However, if you know what you are doing and you want to enable it, do so from the /quasar.config file:
cordova: {
noIosLegacyBuildFlag: true
}The above applies also if you want to specify the build type in your “build.json”.
iOS remote debugging
If you are debugging iOS Apps, you can use the Safari developer tools to remotely debug through a USB cable attached to your iOS phone/tablet. It can be used for emulator too.
This way you have Safari developer tools directly for your App running on the emulator/phone/table. Inspect elements, check console output, and so on and so forth.
First enable the “developer” menu option in the Settings of Safari. Then if you navigate to the “developer” menu option you will see your emulator or connected device listed near the top. From here you can open the developer tools.
Status bar and notch safe-areas
Since mobile phones have a status bar and/or notches, your app’s styling might need some tweaking when building on Cordova. In order to prevent parts of your app from going behind the status bar, there is a global CSS variable that can be used for creating a “safe-area”. This variable can then be applied in your app’s top and bottom padding or margin.
Quasar has support for these CSS safe-areas by default in QHeader/QFooter and Notify. However it’s important to always check your Cordova build on several models to see if all cases of your app are dealing with the safe areas correctly.
In cases you need to manually tweak your CSS you can do so with:
/* for your app's header */
padding-top: constant(safe-area-inset-top); // for iOS 11.0
padding-top: env(safe-area-inset-top); // for iOS 11.2 +
/* for your app's footer */
padding-bottom: constant(safe-area-inset-bottom);
padding-bottom: env(safe-area-inset-bottom);Of course you can also use the above example with margin instead of padding depending on your app.
In order to make sure these are only added when opened on mobile via the Cordova build, you can check for the CSS class .cordova which is automatically added to the body by Quasar. Example:
body.cordova .my-selector {
padding-top: constant(safe-area-inset-top);
padding-top: env(safe-area-inset-top);
}Disabling iOS rubber band effect
When building an iOS app with Cordova and you want to disable the rubber band effect, add this to your /src-cordova/config.xml:
<preference name="DisallowOverscroll" value="true" />